Basic Information & Functions
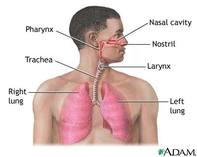
The respiratory system is the system that allows us to breathe. The respiratory system is in charge of gas exchange. We inhale oxygenated air and exhale carbon dioxide waste. With help from the blood in the circulatory system, the oxygen reaches cells all around the body. The blood also carries away waste carbon dioxided that is produced from cellular respiration. Cellular respiration can be breathing at the cellular level. External ventilation is what we think of as breathing. We exhale a gas we do not need and inhale one we do. Cellular respiration entails the oxidization of food molecules in order to form ATP and waste. The waste created by this process is carried away by the blood.
Breaking it down: Level 1: Organs and Structures Involved
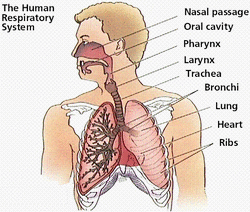
Air enters the body through the nose and mouth (facial structures). Both of theses structures are attached tot he pharynx, or throat. The nos is connected to nasal cavaties that connect to the throat (to be more accurate). These two enterances serve to warm and moisten the air.
Pharynx is synonymous with throat. It connects to the larynx, or voice box.
The larynx connects to the trachea. The outer cartilage on this structure is what is referred to as the Adam's apple (more prevalent in men). This is where the vocal cords are located.
The trachea, otherwise known as the windpipe, is protected by the epiglottis which closes over the trachea when you swallow food. The trachea is covered in cilia which sweep particles out of out the air that is being respirated. Air travels down the trachea to the bronchi.
Air travels to the bronchi (sing. bronchus) comes after the trachea. It divides into two main parts, one going to each lung. They then continue to branch off into more, smaller bronchi. All bronchi are made of cartilage.
Bronchioles are the first airways that are not made of cartilage. They branch off from the bronchi into microscopic tubes. They end in aveoli.
Alveoli are the air sacs that make up the lungs. Each alveoli is convered in a network of capillaries that connect to arteries and veins. Lungs are linked to vessels that deliver oxygen and remove carbon dioxide throughout the body. The pulmonary artery deliver blood saturated in carbon dioxide to the lungs. Inside the alveoli, the carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the air. At the same time, oxygen is infused into the blood ancd carries back to the heart to be pumped all over the body.
Pharynx is synonymous with throat. It connects to the larynx, or voice box.
The larynx connects to the trachea. The outer cartilage on this structure is what is referred to as the Adam's apple (more prevalent in men). This is where the vocal cords are located.
The trachea, otherwise known as the windpipe, is protected by the epiglottis which closes over the trachea when you swallow food. The trachea is covered in cilia which sweep particles out of out the air that is being respirated. Air travels down the trachea to the bronchi.
Air travels to the bronchi (sing. bronchus) comes after the trachea. It divides into two main parts, one going to each lung. They then continue to branch off into more, smaller bronchi. All bronchi are made of cartilage.
Bronchioles are the first airways that are not made of cartilage. They branch off from the bronchi into microscopic tubes. They end in aveoli.
Alveoli are the air sacs that make up the lungs. Each alveoli is convered in a network of capillaries that connect to arteries and veins. Lungs are linked to vessels that deliver oxygen and remove carbon dioxide throughout the body. The pulmonary artery deliver blood saturated in carbon dioxide to the lungs. Inside the alveoli, the carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the air. At the same time, oxygen is infused into the blood ancd carries back to the heart to be pumped all over the body.
Breaking it down: level 2: Muscles involved
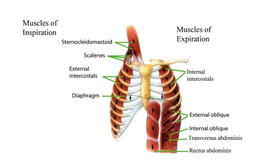
There are muscles located around the lungs that allow for the exapnsion and contraction that is a full breath. Theses muscles are the diaphragm, intercostals, abdominals and muscles in the neck and collarbone area. The diaphragm is a dome shaped muscle located beneath the lungs. It separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. It is the main muscle associated iwth breathing. The intercostals are located between the ribs. Abdominal muscles are located below the diaphragm and assist in rapid breathing. Muscles in your neck and collar bone help you breathe when your lungs or other muscles involved with breathing are not working so well.
