Functions & Fun Facts
The cardiovascular system is comprised of the heart and blood. The heart is a fist sized muscular organ in your chest that is responsible for pumping blood all over the body. The blood carries oxygen from the lungs and nutrients from the digestive system to the cells all over the body. Then, the blood carries the cell's metabolic wastes and carbon dioxide away from the cell. The kidneys then filter these things out of the blood. Blood helps maintain a body's normal temperature, carries and delivers horomones to cells, sends antibodies to fight infection and has clotting factors that help with making vlots and healing tissues. Blood not only contains horomones but fats, carbohydrates, protein and gases.The average adult male has 10-12 pints of blood. The average woman has 8-9 pints of blood. Blood is actually a tissue. It is made of 80% water and 20% cells.
Breaking it Down: Level One: The Heart
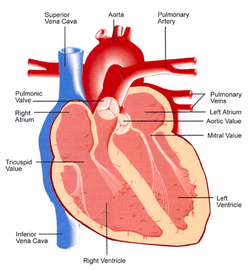
The right atrium, which used to be known as the right auricle, receives deoxygenated blood from the vena cava. It then pumps the blood into the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve.
The right ventricle, the lower chamber of the right side of the heart, receives blood from the right atrium. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs so it can be oxygenated.
The left atrium recieves oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins (from the lungs) and pumps it into the left ventricle through the atrioventricular valve.
The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium. It the contracts (systole) to pump blood through the aorta.
The vena cava is separated into the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. The superior vena cava is the large vein that carries blood from the head, neck and upper limbs to the heart. The inferior vena cava delivers blood from the lower body to the heart.
The pulmonic valve is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. It opens in ventricular systole when right ventricle pressure rises above that in the pulmonary artery.
The tricuspid valve is located between the right atrium and the right ventricle. It usually has three leaflets and three papillary muscles. It is the first valve blood encounters once it enters the heart.
The mitral, or bicuspid, valve is found between the left atrium and the left ventricle. It allows for blood to flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle. It has two flaps and is called mitral because it resembles a bishop's headdress, called a miter.
The aortic valve is situated at the exit of the left ventricle where the aorta begins. This valve allows for blood to flow from the left ventricle into the aorta and prevents blood in the aorta from flowing back into the heart.
Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium. They are the only veins that carry the bright red, or oxygenated, blood.
The pulmonary artery is one of two branches that form the pulmonary trunk. There is a right one and a left one. Both carry oxygen poor blood to the the lungs.
The aorta is the largest valve artery in the body. It goes down through the chest where it divides into two arterie that go the legs. It supplies head, neck, arms, major organs inthe chest and abdomen and the legs with oxygenated blood.
The pericardium is a fibrous sac that surrounds the heart and the roots of the largest blood vessels.The outer layer, or parietal pericardium, is thick and tough and loosely surrounds the heart. The inner coat, or visceral pericardium, is a bilayered film that adheres directly to the heart. The space between theses layers is filled with pericardial fluid,
The right ventricle, the lower chamber of the right side of the heart, receives blood from the right atrium. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs so it can be oxygenated.
The left atrium recieves oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins (from the lungs) and pumps it into the left ventricle through the atrioventricular valve.
The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium. It the contracts (systole) to pump blood through the aorta.
The vena cava is separated into the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. The superior vena cava is the large vein that carries blood from the head, neck and upper limbs to the heart. The inferior vena cava delivers blood from the lower body to the heart.
The pulmonic valve is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. It opens in ventricular systole when right ventricle pressure rises above that in the pulmonary artery.
The tricuspid valve is located between the right atrium and the right ventricle. It usually has three leaflets and three papillary muscles. It is the first valve blood encounters once it enters the heart.
The mitral, or bicuspid, valve is found between the left atrium and the left ventricle. It allows for blood to flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle. It has two flaps and is called mitral because it resembles a bishop's headdress, called a miter.
The aortic valve is situated at the exit of the left ventricle where the aorta begins. This valve allows for blood to flow from the left ventricle into the aorta and prevents blood in the aorta from flowing back into the heart.
Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium. They are the only veins that carry the bright red, or oxygenated, blood.
The pulmonary artery is one of two branches that form the pulmonary trunk. There is a right one and a left one. Both carry oxygen poor blood to the the lungs.
The aorta is the largest valve artery in the body. It goes down through the chest where it divides into two arterie that go the legs. It supplies head, neck, arms, major organs inthe chest and abdomen and the legs with oxygenated blood.
The pericardium is a fibrous sac that surrounds the heart and the roots of the largest blood vessels.The outer layer, or parietal pericardium, is thick and tough and loosely surrounds the heart. The inner coat, or visceral pericardium, is a bilayered film that adheres directly to the heart. The space between theses layers is filled with pericardial fluid,
Breaking it Down: Level Two: Veins, Arteries & Capillaries
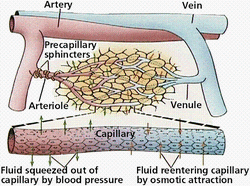
Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart. Oxyhemoglobin, or oxygenated hemoglobin, is what gives arteries their bright red color.
A vein is a blood vessel that carries blood low in oxygen from the body back to the heart. The purple-blue deoxyhemoglobin in the blood is what makes veins appear to be dark.
Capillaries are the smallest of all the vessels and attach the smallest components of arteries, arterioles, to the smallest compenents of veins, or venules. The capillaries form a network all over the body.
A vein is a blood vessel that carries blood low in oxygen from the body back to the heart. The purple-blue deoxyhemoglobin in the blood is what makes veins appear to be dark.
Capillaries are the smallest of all the vessels and attach the smallest components of arteries, arterioles, to the smallest compenents of veins, or venules. The capillaries form a network all over the body.
Breaking it Down: Level Three: Blood & its Components
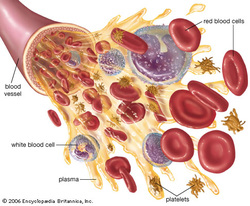
Blood is 80% water and 20% cells:
Plasma is "the yellowish stuff" and is 90% water. Blood is mostly plasma. A plasma cell is a fully differentiated lymphocyte in the B-cell lineage.It is a type of white blood cells that produce and secrete antibodies.
Red blood cells are the cells that carry oxygen. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, the oxygen carrying pigment and predominate protein in red blood cells that forms reversible and unstable bonds with oxygen, and transport carbon dioxide away from cells and deliver oxygen to cells. Red blood cells are made in the bone marrow.
White blood cells are the blood cells that help fight infection. Two common types of white blood cells are lymphocytes and neutrophils. Lymphocytes are made in the lymphoid tissue in the spleen, lymph nodes and thymus gland. They identify foreign substances from germs, bacterias or viruses and produce targeted anitbodies. Neutrophils are made in the bone marrow and circulate through the blood stream. Neutrophils actually move out of blood vessels and into infected tissues. The pus in a boil is made largely of neutrophils.
Plateles are irregularly shaped, sticky, coreless bodies that form clots to stop bleeding. Platelets gather around a wound to form a clot. A clot begins to form once exposed to air. The platelets react to the air and begin to break apart. Then they react with the fibrinogen to form tiny, thread-like fibrin. The fibrin begin to form a mesh that traps blood cells in it. The mesh hardens and dries into a scab.
Plasma is "the yellowish stuff" and is 90% water. Blood is mostly plasma. A plasma cell is a fully differentiated lymphocyte in the B-cell lineage.It is a type of white blood cells that produce and secrete antibodies.
Red blood cells are the cells that carry oxygen. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, the oxygen carrying pigment and predominate protein in red blood cells that forms reversible and unstable bonds with oxygen, and transport carbon dioxide away from cells and deliver oxygen to cells. Red blood cells are made in the bone marrow.
White blood cells are the blood cells that help fight infection. Two common types of white blood cells are lymphocytes and neutrophils. Lymphocytes are made in the lymphoid tissue in the spleen, lymph nodes and thymus gland. They identify foreign substances from germs, bacterias or viruses and produce targeted anitbodies. Neutrophils are made in the bone marrow and circulate through the blood stream. Neutrophils actually move out of blood vessels and into infected tissues. The pus in a boil is made largely of neutrophils.
Plateles are irregularly shaped, sticky, coreless bodies that form clots to stop bleeding. Platelets gather around a wound to form a clot. A clot begins to form once exposed to air. The platelets react to the air and begin to break apart. Then they react with the fibrinogen to form tiny, thread-like fibrin. The fibrin begin to form a mesh that traps blood cells in it. The mesh hardens and dries into a scab.
Second Helping: Cardiovascular Disease
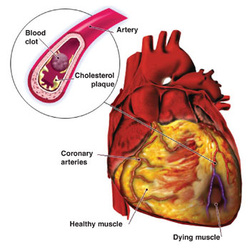
Cardiovascular disease refers to a cluster of diseases that affect the heart and blood vessels. Cardiovascular diesase is the number one killer in the U.S. and worldwide. About 29.34% of deaths annualy are the result of this cluster of diseases. Artherosclerosis, a condition where the walls of the arties thicken due to a build up of fatty plaque, is what people intend to say when they say someone has a cardiovascular disease. Once it is detected, most of the time it is pretty advanced because te plaque has been building up for decades. A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, is when the blood supply to the heart is interrupted because the buildup in an artery has blocked the supply of blood to the heart. The resultng ischemia, or shortage of blood, causes oxygen not to be delivered to heart muscle cells. Heart tissue begins to die and if the problem is not remedied the person having a heart attack could die due to heart failure.
Image Citations
http://www.nextscience.org/tech/the-heart-that-is-able-to-make-calls/
http://www.niaaa.nih.gov/RESOURCES/GRAPHICSGALLERY/CARDIOVASCULARSYSTEM/Pages/DiagramofHeart.aspx
http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/biobookcircsys.html
http://homeworkteam71.wikispaces.com/Science+with+Mr.+Mullett
http://www.topnews.in/health/cardiovascular-disease-can-have-its-roots-early-childhood-26170
http://www.niaaa.nih.gov/RESOURCES/GRAPHICSGALLERY/CARDIOVASCULARSYSTEM/Pages/DiagramofHeart.aspx
http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/biobookcircsys.html
http://homeworkteam71.wikispaces.com/Science+with+Mr.+Mullett
http://www.topnews.in/health/cardiovascular-disease-can-have-its-roots-early-childhood-26170
