Basic Information & Functions

There are over 600 muscles all of varying size, shape and function, throughout the human body. Muscles are made of soft, contractile tissue that cover the entire skeletal system. Muscles are attached to bones via tendons. Muscles and bones combine to form the musculoskeletal system that allows for movement. Muscles work in pairs to flex and extend to allow movement to occur. Movement is the muscular system's main function. Muscles also maintain posture by supporting the bones that allow humans to stand upright. Muscles also carry out digestion. Muscles help with thermoregulation through their movement. When a muscle moves, it creates heat. When a person gets to cold, the muscles will move involuntarily to create heat.
Breaking it Down: The Three Muscle Types
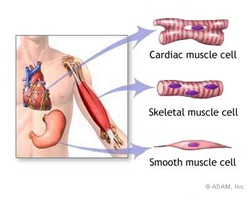
Skeletal muscle are called striated muscles because they appear to be striped, or made of bands. Skeletal muscle are voluntary and responsible for movements like running and jumping. They are attached to bones via tendons.
Smooth muscles are the type of muscles that organs are made of. Smooth muscles are also involuntary muscles such as the stomach and bladder.
Cardiac muscle cells make the myocardium (heart). This muscle has to be very strong because it never stops beating throughout an organisms entire lifespan. It is also an involuntary muscle.
Smooth muscles are the type of muscles that organs are made of. Smooth muscles are also involuntary muscles such as the stomach and bladder.
Cardiac muscle cells make the myocardium (heart). This muscle has to be very strong because it never stops beating throughout an organisms entire lifespan. It is also an involuntary muscle.
Second Helping: Myosin & Actin
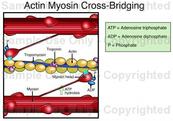
Actin is a muscle cell protein that allows muscles to move. Myosin is a motor protein that is responsible for actin based motility or or the ability to move spontaneously because Myosin delivers ATP to actin. Through a collaboartive effort, actin and myosin allow for muscle movement.
